Difference stuttering and cluttering
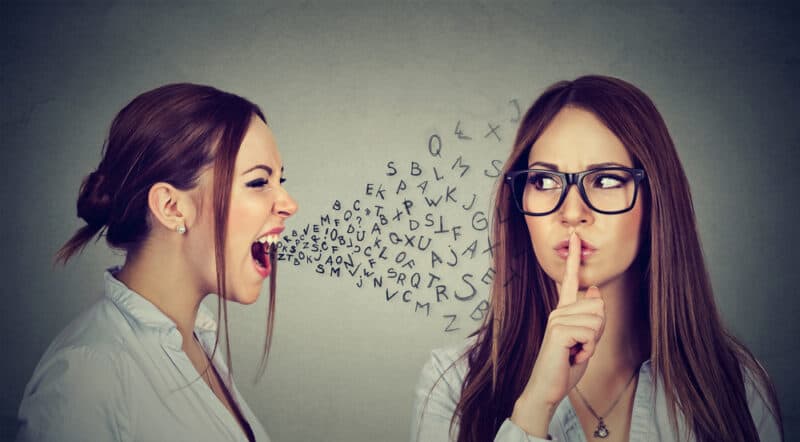
Scientists around the world agree that cluttering is something (completely) different from stuttering. But what, exactly, are the differences between the two fluency disorders? And are there any similarities? To answer the latter question; yes, there are. For example, repetitions, interjections and tachylaly (speaking too fast) can be found in both cluttering and stuttering. There are, however, also clear differences between the two speech impediment,emts. And the differences are undoubtedly in the majority. We can’t mention enough, though, that there is also a mixed form, called clutter-stuttering. Someone who clutter-stutters shows features of both disorders.

Basic difference stuttering and cluttering
Stuttering and cluttering differ on a fundamental level. For example, one of the most striking notions is that stuttering speakers struggle to say what has already been planned, whereas in cluttering this language planning is not yet complete. This difference shows directly in their speech output: stuttering speakers show tensed blockages or prolongations in their speech (also known as “stuttering-like disfluencies”), involving “fighting behavior”. As opposed to stuttering the disfluencies in the speech of cluttering speakers are different in nature and come out in a relaxed manner. That’s why they are also called “normal (typical) disfluencies”.
In addition to that it is important to know that people who stutter are more aware of the imperfections in their speech than cluttering speakers. This is the reason why stuttering speakers often have fear of talking, as opposed to cluttering speakers. However, communication fear can also arise in cluttering speakers, the fear of not being understood by others. You will read everything about cluttering in the book Too fast for words.
So, it isn’t speech alone?
Because speech impediment cluttering is fundamentally all about language planning, cluttering is not only about speech – in its most narrow definition – alone. This shows for example in the following symptoms. When people who clutter concentrate well on their speech, their speech improves immediately; this is the other way around for stuttering speakers. Also, on difficult topics of conversation, cluttering speakers often have trouble to get out of their words easily; for people who stutter the difficulty of the subject does not matter. Furthermore, speech of cluttering speakers often improves when speaking in a foreign language. This gets worse in stuttering speakers. In addition, reading aloud an unknown text is beneficial for people who clutter; while it isn’t for people who stutter. This is the other way around when reading a known text aloud.
Cluttering symptoms also show in the physical appearance (body language) of cluttering speakers; they come across a lot more restless than stuttering speakers. Former scientist and speech-language therapist Deso Weiss put together an overview based on dozens of years of clinical experience, which he used in differential diagnoses. Can you use some help with your cluttering? See our coaching options.
| Points of difference | Cluttering | Stuttering |
|---|---|---|
| Self-awareness | Poor to none | Good |
| Speaking under stress | Better | Worse |
| Speaking when relaxed | Worse | Better |
| Concentrating on speech | Better | Worse |
| Speaking after being interrupted | Better | Worse |
| Giving short answers | Better | Worse |
| Speaking in foreign language | Better | Worse |
| Reading aloud known text | Worse | Better |
| Reading aloud unknown text | Better | Worse |
| Handwriting | Hasty, uninhibited | Forced, inhibited |
| Attitude towards speaking | Indifferent | Worried |
| Psychological attitude | Extraverted | Introverted |
| Goal for therapy | Focus on details | Focus derived from details |
Do I clutter?
Are you doubting whether you clutter, stutter of have characteristics of both speech disorders? No problem; take the self-test. This easy, fast and comprehensible tool gives a preliminary result in just minutes. Make sure to always consult a professional (speech-language pathologist) afterwards. You can also come to us for coaching.